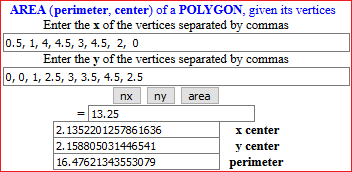
Example:

The graph with WolframAlpha:
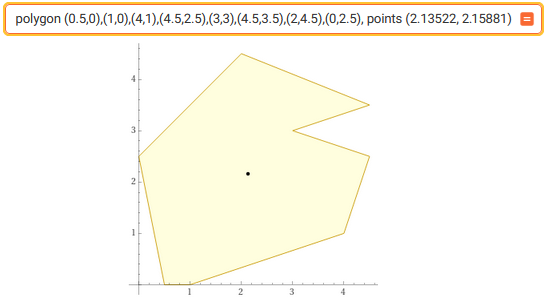
The centroid, also known as geometric center or center of plane figure F, is the center of mass (or barycenter) of a lamina of constant thickness and of a single material having the shape of F. In other words, it is the point at which a cutout of the shape F (with uniformly distributed mass) could be perfectly balanced on the tip of a pin.
Come è calcolata l'area?
vedi
Il centroide (che nel caso di una figura piatta di materiale omogeneo coincide col baricentro) C di un poliogno
C
C
Nota. Non ha alcun senso parlare di angoli esterni di un poligono. A parte il fatto che non sono angoli del poligono, nel caso del poligono sopra raffigurato quali sarebbero? È una delle tante nozioni inutili o errate che vengono spesso fatte studiare a scuola, per buttar via tempo e non affrontare argomenti più importanti.